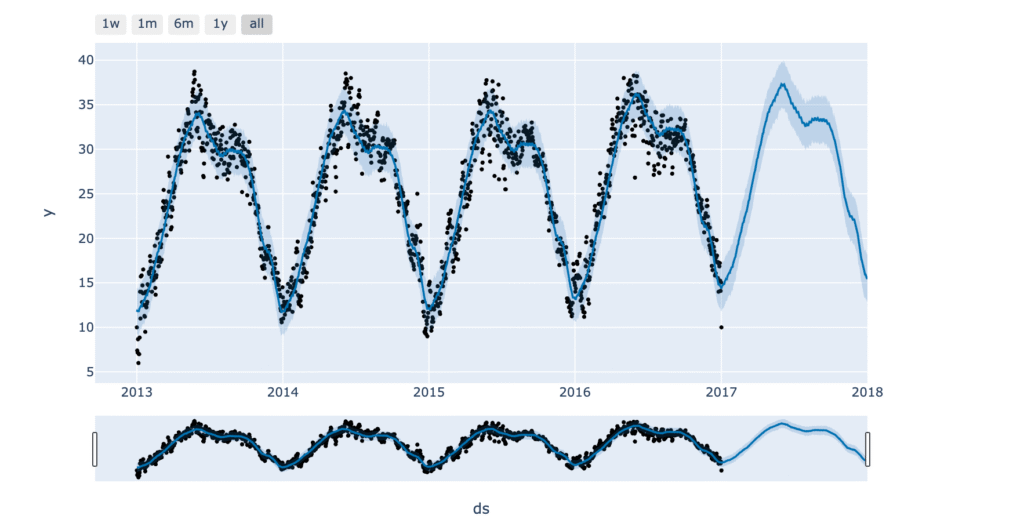
Weather forecasting involves predicting the atmospheric conditions of a specific location for a particular period. By utilising historical weather data and predictive algorithms, it’s possible to estimate weather patterns for the upcoming days. To forecast weather using Python, we need a dataset that includes past weather records for a chosen location. We are using a dataset from Kaggle containing daily weather data for New Delhi, which can be used for this forecasting task. You can download the dataset from here.
Let’s analyse the data and predict weather conditions using Python.
Data Exploration
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import plotly.express as px
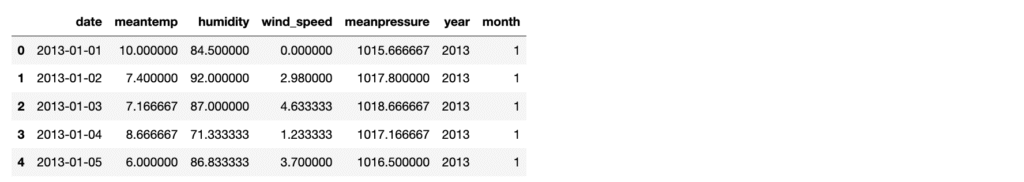
data=pd.read_csv("/Users/rahul_anand/Downloads/DailyDelhiClimateTrain.csv")
data.head()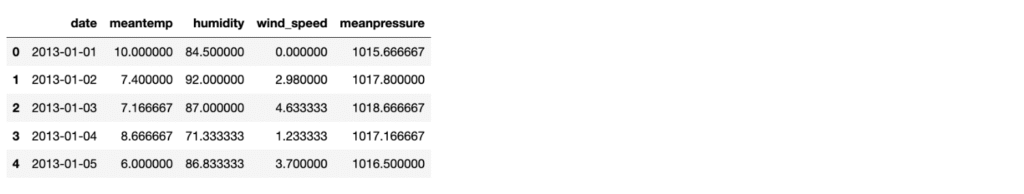
Let’s explore the descriptive statistics of the data
data.describe()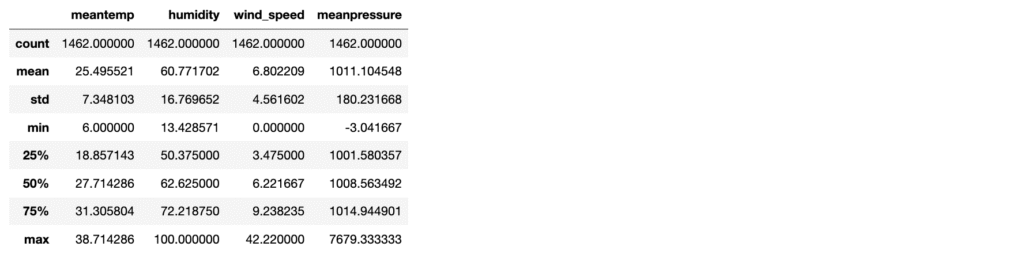
Now let’s explore the information about all the columns in the dataset:
data.info()
The date column in this dataset is not having a datetime data type. We will change it when required.
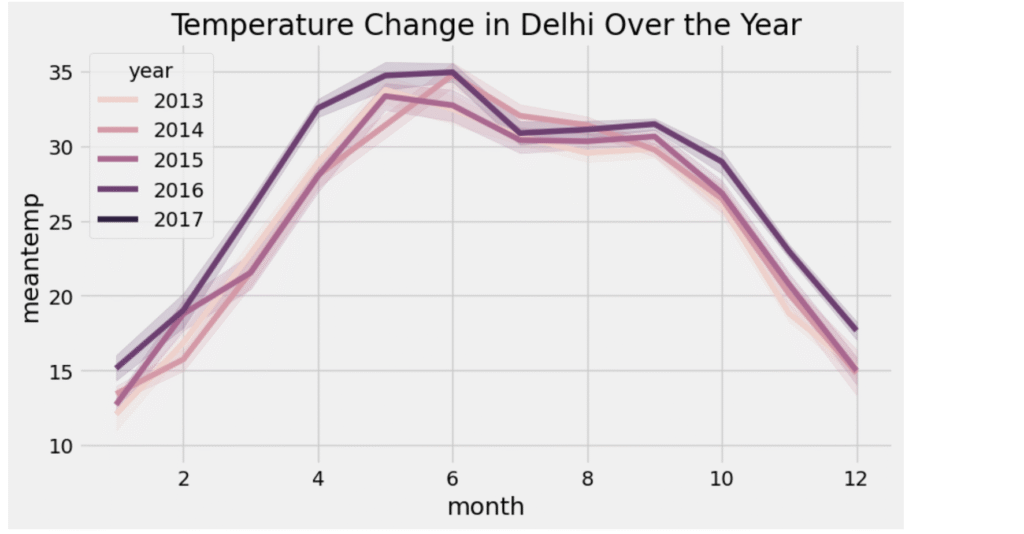
Now, let’s explore the mean temperature in Delhi over the years:
figure = px.area(data, x="date",
y="meantemp",
title='Mean Temperature in Delhi Over the Years')
figure.show()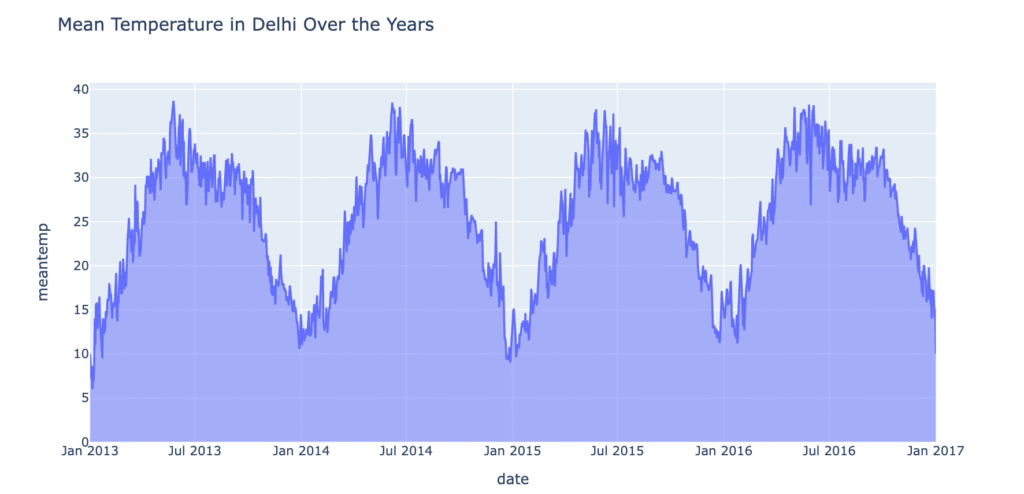
There is not much difference between mean temperature over the year. Its almost following the same pattern every year with 35-40 in July and 10-15 in Jan.
Let’s analyze the humidity in Delhi over the years:
fig=px.area(data,
x="date",
y="humidity",
title='Humdity in Delhi Over the Years')
fig.show()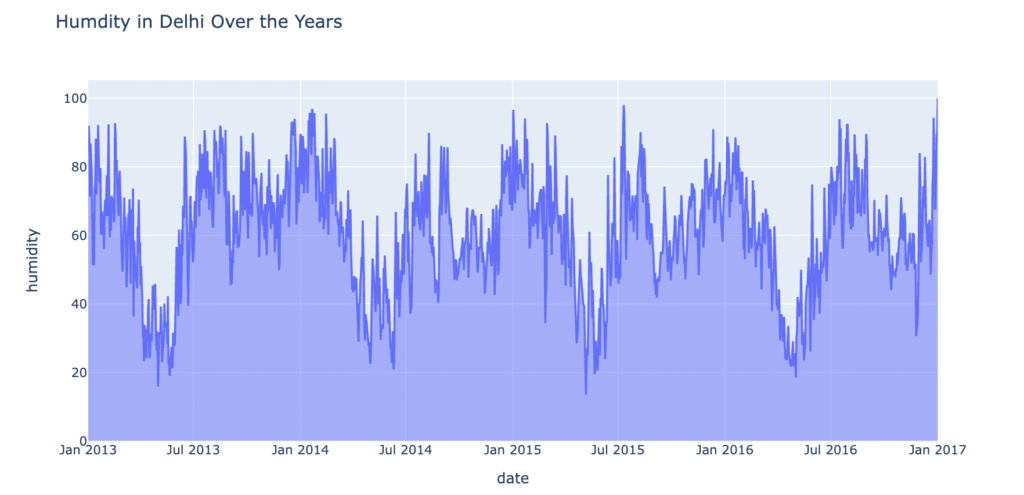
There is a clear repeating yearly cycle in humidity levels. Humidity levels spike between June and September, which corresponds to Delhi’s monsoon season. Each year follows a relatively similar pattern. There is no evident long-term upward or downward trend, implying that average annual humidity remained stable during the 2013–2017 period.
Now let’s see the wind speed in Delhi over the years:
fig=px.area(data,
x="date",
y="wind_speed",
title="Wind Speed in Delhi Over the Years")
fig.show()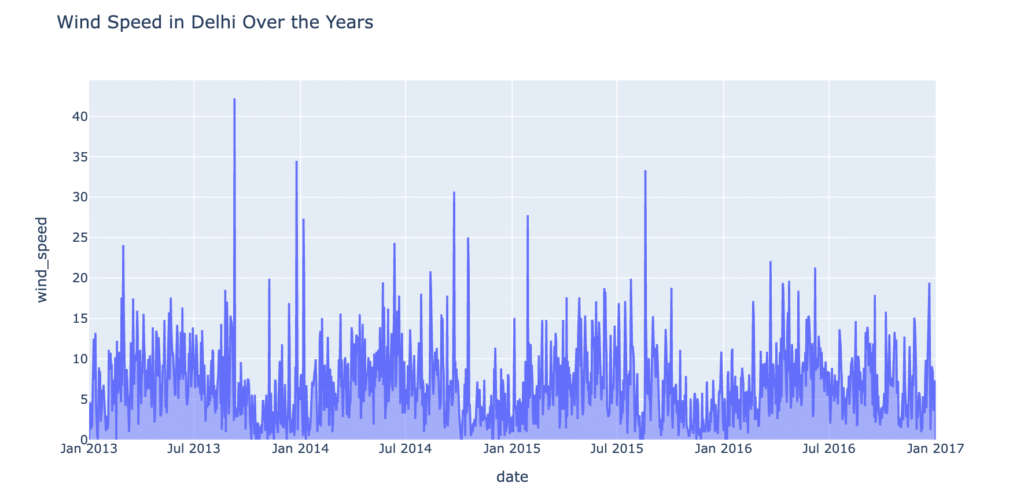
Until 2015, wind speeds were generally higher during the monsoon months (August and September) and the retreating monsoon period (December and January). However, after 2015, no unusual variations in wind speed were observed during the monsoons.
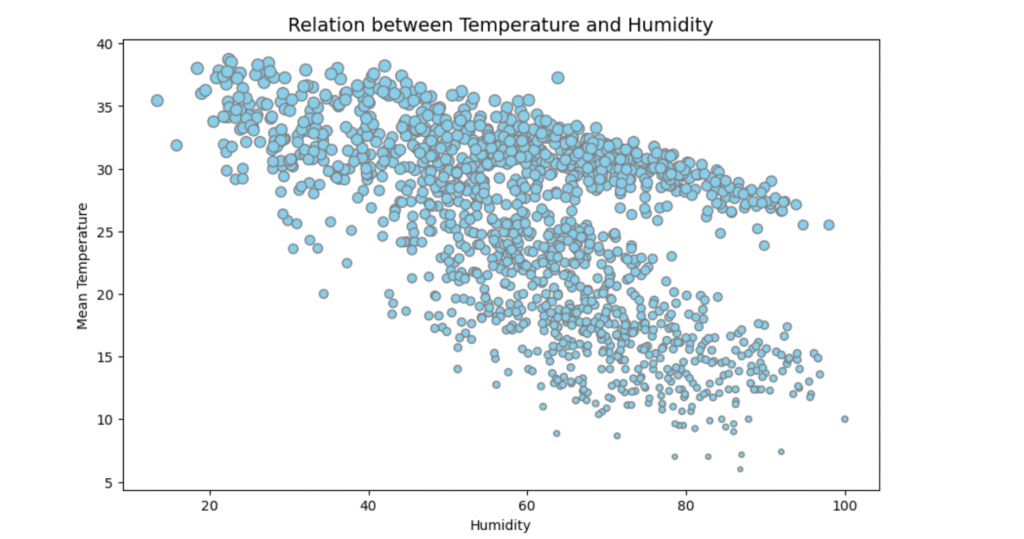
Now, let’s examine the relationship between temperature and humidity.
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
scatter = plt.scatter(data['humidity'],
data['meantemp'],
s=data['meantemp'] * 2, # scale size for visibility
c='skyblue',
edgecolors='gray')
plt.title("Relation between Temperature and Humidity", fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel("Humidity")
plt.ylabel("Mean Temperature")